MFG Day 2020: Capital Region Metros Lead NYS in Manufacturing Minority Worker Growth
The manufacturing sectors of the Capital Region’s major metropolitan areas are growing their ranks of minority workers more rapidly than those of other metros in the state. As a result of this growth, the Albany-Schenectady-Troy metropolitan statistical area (MSA) has gone from having the state’s fourth most racially diverse manufacturing sector in 2010 to the second most racially diverse in 2019, according to a Center for Economic Growth (CEG) analysis of U.S. Census Bureau data.
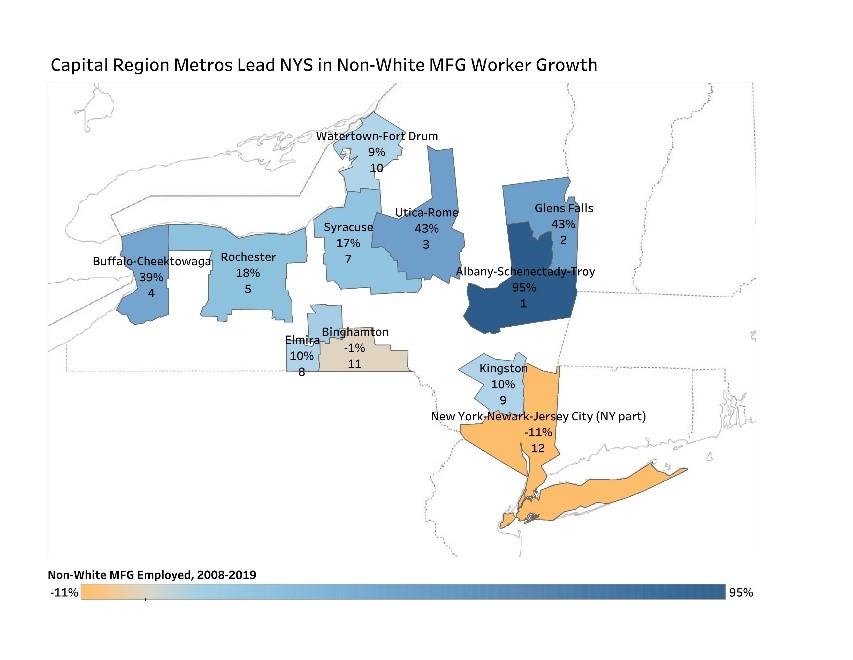
Racial MFG Diversity
Over the past 10 years, the Albany-Schenectady-Troy and Glens Falls metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs) have seen tremendous growth in both the racial and ethnic makeup of their manufacturing workforce. Between 2008 and 2019, the Albany-Schenectady-Troy MSA saw its non-white manufacturing workforce increase by 94.8 percent to 4,190, and the Glen’s Falls MSA’s non-white manufacturing workforce grew by 43.2 percent to 199. By 2019, 15.9 percent of the Albany-Schenectady-Troy MSA’s manufacturing sector was not white, compared to 10.5 percent 10 years earlier. Among the state’s dozen metros, only the New York-Newark-Jersey City MSA (NY part) had a more racially diverse manufacturing sector at 30 percent last year.

Ethnic MFG Diversity
During the 10-year period, the Albany-Schenectady-Troy and Glens Falls MSAs’ manufacturing sectors also led the state in growing their ranks of Hispanic or Latino workers, increasing by 103.1 percent to 1,495 and by 62 percent to 115, respectively. Within the Albany-Schenectady-Troy MSA, no other major sector (excluding mining, quarrying, and oil and gas extraction) had a faster growing non-white and Hispanic or Latino workforce than manufacturing. By 2019, 5.7 percent of the Albany-Schenectady-Troy MSA’s manufacturing sector was Hispanic or Latino, compared to 3.6 percent 10 years earlier.
Sector Diversity
In the Capital Region, manufacturing is not only presenting significant career opportunities for minorities, but also for young workers. CEG research has shown manufacturing had the Albany-Schenectady-Troy MSA’s second fastest growth rate for young workers (19 to 34 years old) among all major sectors, increasing 10.2 percent over the past five years. Only healthcare had a stronger growth rate at 11.1 percent. But among non-white and Hispanic or Latino workers in the Albany-Schenectady-Troy MSA, no other sector had a stronger growth rate over the past 10 years than manufacturing.

Opportunities amid COVID-19
Amid the coronavirus pandemic, many manufacturers demonstrated their essential nature by continuing to operate while most other businesses were forced to close their in-person, non-essential operations. And six months after the lockdown began, demand for talent remains strong in manufacturing. As of August and throughout the eight counties, there were 126 postings for production jobs, according to data from the New York State Department of Labor.
Several new training programs are helping young workers enter or advance in manufacturing careers. CEG supports the following:
Hudson Valley Community College’s Manufacturing Technology Pathways Project, a short-term, stackable credential training program, or “boot camp,”
SUNY Schenectady’s Certified Production Technician (CPT) program, a certificate course that skills up incumbent workers who are looking to advance their career, or enhance the education of unemployed or underemployed persons with manufacturing backgrounds.
The Capital Region Manufacturing Intermediary Apprenticeship Program (MIAP) to assist local manufacturers in training workers for high-skill trades. Since this program launched in 2018, CEG has onboarded more than two dozen apprentices as local manufacturers such as Beech-Nut in Florida, Electrometrics in Johnstown, Espey Mfg. & Electronics Corp in Saratoga Springs, Greno Industries in Scotia, and Plug Power in Latham.
CEG’s Business Growth Solutions (BGS) offers technical services to help Capital Region manufacturers with operational improvement, strategic growth, sustainability and energy efficiency, and technology acceleration.
SEMI’s Industry Approved Apprenticeship Program (IAAP), a first-of-its-kind program that will train 50 workers at GLOBALFOUNDRIES’ Fab8 in skills demanded by the electronics industry.
Other new programs include Capital Region BOCES’ engineering technician program, which provides training for technical careers in engineers and has a curriculum that supports employment at GLOBALFOUNDRIES. BOCES’s adult welding also trains students for careers in manufacturing.
Don’t miss these insights into the trends that are shaping the Capital Region’s economy. Sign up for CEG’s e-news and follow us on: